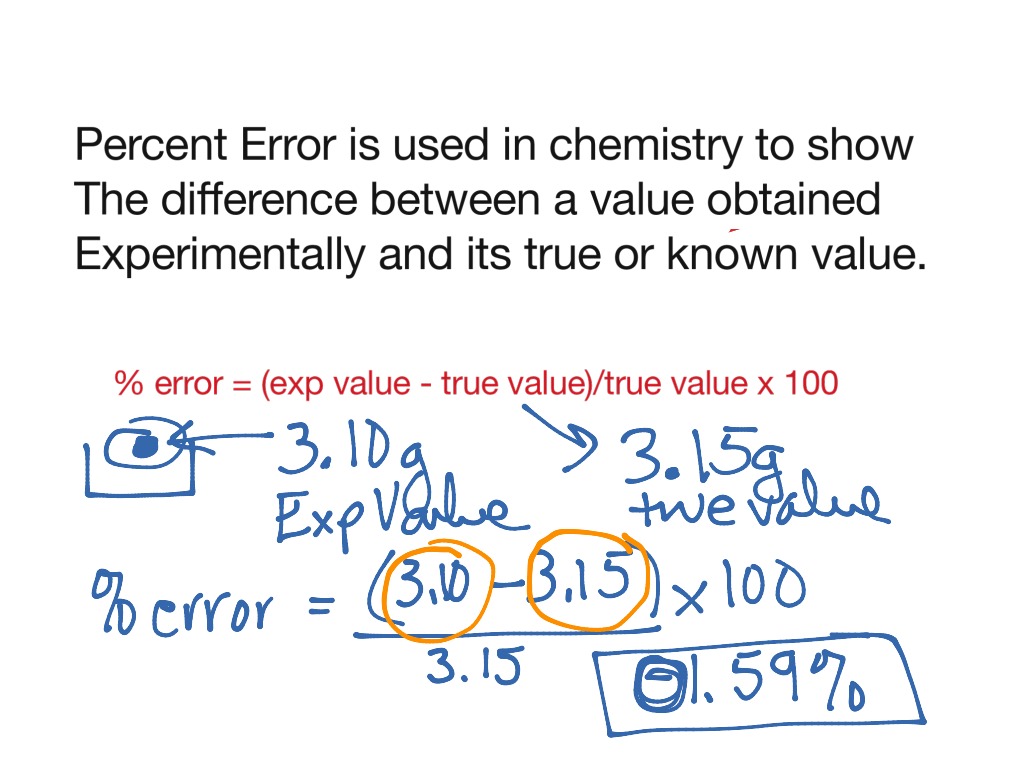
Definition Of Error In Chemistry . As discussed earlier, we divide errors into determinate and. All measurements have errors associated with them. Random error and systematic error. These errors fall into two categories: Take a look at what systematic and. “lies, damn lies, and statistics.” chem m3lc lectures week 1. There are two broad classes of observational errors: In other words, error is a measure of bias. Random error varies unpredictably from one. It naturally results from the instruments we use, the way we use them, and factors outside our control. Error is not an accident or mistake. Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a measured value and the known or accepted value. Error is the difference between a single measurement or result and its expected value. To illustrate how the number of significant digits indicates the error, suppose we had a measurement reported as 3.42 g.
from www.showme.com
Random error and systematic error. Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a measured value and the known or accepted value. In other words, error is a measure of bias. Take a look at what systematic and. As discussed earlier, we divide errors into determinate and. Random error varies unpredictably from one. To illustrate how the number of significant digits indicates the error, suppose we had a measurement reported as 3.42 g. All measurements have errors associated with them. These errors fall into two categories: It naturally results from the instruments we use, the way we use them, and factors outside our control.
Percent Error chemistry Science, Chemistry, Measurements and
Definition Of Error In Chemistry There are two broad classes of observational errors: Random error varies unpredictably from one. Error is the difference between a single measurement or result and its expected value. These errors fall into two categories: There are two broad classes of observational errors: All measurements have errors associated with them. As discussed earlier, we divide errors into determinate and. Random error and systematic error. Error is not an accident or mistake. In other words, error is a measure of bias. It naturally results from the instruments we use, the way we use them, and factors outside our control. Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a measured value and the known or accepted value. Take a look at what systematic and. “lies, damn lies, and statistics.” chem m3lc lectures week 1. To illustrate how the number of significant digits indicates the error, suppose we had a measurement reported as 3.42 g.
From www.vrogue.co
What Is Measurement Error Definition Types Of Errors In Measurement Definition Of Error In Chemistry There are two broad classes of observational errors: As discussed earlier, we divide errors into determinate and. Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a measured value and the known or accepted value. Error is not an accident or mistake. In other words, error is a measure of bias. These errors fall. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From sciencenotes.org
Absolute and Relative Error and How to Calculate Them Definition Of Error In Chemistry These errors fall into two categories: Take a look at what systematic and. Random error and systematic error. It naturally results from the instruments we use, the way we use them, and factors outside our control. Random error varies unpredictably from one. There are two broad classes of observational errors: Error is the difference between a single measurement or result. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From siliconvalleygazette.com
You have a problem with device chemistry failure Silicon Valley Gazette Definition Of Error In Chemistry Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a measured value and the known or accepted value. Random error and systematic error. It naturally results from the instruments we use, the way we use them, and factors outside our control. As discussed earlier, we divide errors into determinate and. Take a look at. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From www.expii.com
Types of Error — Overview & Comparison Expii Definition Of Error In Chemistry It naturally results from the instruments we use, the way we use them, and factors outside our control. To illustrate how the number of significant digits indicates the error, suppose we had a measurement reported as 3.42 g. In other words, error is a measure of bias. All measurements have errors associated with them. Random error varies unpredictably from one.. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From ksa.mytutorsource.com
Percentage Error Formula, Definition, How to Calculate It! Definition Of Error In Chemistry Error is the difference between a single measurement or result and its expected value. There are two broad classes of observational errors: These errors fall into two categories: It naturally results from the instruments we use, the way we use them, and factors outside our control. To illustrate how the number of significant digits indicates the error, suppose we had. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From siliconvalleygazette.com
You have a problem with device chemistry failure Silicon Valley Gazette Definition Of Error In Chemistry Random error and systematic error. As discussed earlier, we divide errors into determinate and. Error is the difference between a single measurement or result and its expected value. In other words, error is a measure of bias. Take a look at what systematic and. There are two broad classes of observational errors: Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error,. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From www.pinterest.com.au
Chemistry Tutorial Experimental Errors Chemistry, Science chemistry Definition Of Error In Chemistry It naturally results from the instruments we use, the way we use them, and factors outside our control. Random error and systematic error. Random error varies unpredictably from one. There are two broad classes of observational errors: To illustrate how the number of significant digits indicates the error, suppose we had a measurement reported as 3.42 g. “lies, damn lies,. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From sciencenotes.org
Systematic vs Random Error Differences and Examples Definition Of Error In Chemistry Random error and systematic error. Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a measured value and the known or accepted value. Random error varies unpredictably from one. Error is not an accident or mistake. All measurements have errors associated with them. There are two broad classes of observational errors: “lies, damn lies,. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
Spotting procedural errors in chemistry practicals YouTube Definition Of Error In Chemistry There are two broad classes of observational errors: It naturally results from the instruments we use, the way we use them, and factors outside our control. Error is the difference between a single measurement or result and its expected value. All measurements have errors associated with them. Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From chemistnotes.com
Errors in Chemical Analysis Determinate and Indeterminate Errors Definition Of Error In Chemistry Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a measured value and the known or accepted value. Take a look at what systematic and. Error is the difference between a single measurement or result and its expected value. All measurements have errors associated with them. In other words, error is a measure of. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From math.wonderhowto.com
How to Calculate percent error in chemistry lab activities « Math Definition Of Error In Chemistry Random error and systematic error. Error is the difference between a single measurement or result and its expected value. As discussed earlier, we divide errors into determinate and. Random error varies unpredictably from one. Error is not an accident or mistake. In other words, error is a measure of bias. To illustrate how the number of significant digits indicates the. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
Introduction to Error Analysis for Chemistry Lab YouTube Definition Of Error In Chemistry Error is not an accident or mistake. In other words, error is a measure of bias. Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a measured value and the known or accepted value. All measurements have errors associated with them. To illustrate how the number of significant digits indicates the error, suppose we. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From www.showme.com
Percent and Relative Error Science, Chemistry, Physics ShowMe Definition Of Error In Chemistry Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a measured value and the known or accepted value. In other words, error is a measure of bias. Error is the difference between a single measurement or result and its expected value. “lies, damn lies, and statistics.” chem m3lc lectures week 1. It naturally results. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From bugmannd2jmaterialdb.z13.web.core.windows.net
Percent Error Worksheet Chemistry Definition Of Error In Chemistry These errors fall into two categories: Random error varies unpredictably from one. Random error and systematic error. “lies, damn lies, and statistics.” chem m3lc lectures week 1. It naturally results from the instruments we use, the way we use them, and factors outside our control. Take a look at what systematic and. All measurements have errors associated with them. In. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From www.tessshebaylo.com
Equation For Percent Error In Chemistry Tessshebaylo Definition Of Error In Chemistry Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a measured value and the known or accepted value. All measurements have errors associated with them. Random error and systematic error. There are two broad classes of observational errors: As discussed earlier, we divide errors into determinate and. These errors fall into two categories: To. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From kizasupplier.weebly.com
Percent error chemistry calculator kizasupplier Definition Of Error In Chemistry These errors fall into two categories: Take a look at what systematic and. “lies, damn lies, and statistics.” chem m3lc lectures week 1. Error is the difference between a single measurement or result and its expected value. Error is not an accident or mistake. Percent error, sometimes referred to as percentage error, is an expression of the difference between a. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Experimental Error PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Definition Of Error In Chemistry Error is the difference between a single measurement or result and its expected value. Error is not an accident or mistake. “lies, damn lies, and statistics.” chem m3lc lectures week 1. All measurements have errors associated with them. There are two broad classes of observational errors: In other words, error is a measure of bias. Take a look at what. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
11.1 Random and systematic errors (SL) YouTube Definition Of Error In Chemistry Random error and systematic error. “lies, damn lies, and statistics.” chem m3lc lectures week 1. To illustrate how the number of significant digits indicates the error, suppose we had a measurement reported as 3.42 g. Take a look at what systematic and. As discussed earlier, we divide errors into determinate and. It naturally results from the instruments we use, the. Definition Of Error In Chemistry.